Olá!
O Anel do Sul:
Uma nebulosa planetária com uma estrela central muito brilhante
Argo Navis, o (antigo) Navio
- hoje desmembrado em Popa, Quilha e Vela -
é uma constelação que sempre nos traz muitas surpresas.
Uma dica bem interessante é começar sua viagem pelo Gigante Caçador, Orion
(não tem quem não conheça e reconheça esta constelação,
sempre nos apresentando suas três estrelinhas
chamadas popularmente de As Três Marias!)
e então ser "chamado" pelo brilho intenso
da estrela-alpha Canis Majoris,
Sirius.
Perceba então que existem algumas estrelas tímidas
como se formassem um paredão, algo assim: é a Popa, Puppis, do Navio!
A partir da Popa,
não tem como não ser "chamado" pela estrela-alpha do antigo Navio
e da recente Quilha, Carina,
a bela Canopus, o capitão do Navio.
A Vela chama nossa atenção
- a olho nú -
por figurar exatamente como a mesma,
sem tirar nem por.
- a olho nú -
por figurar exatamente como a mesma,
sem tirar nem por.
No entanto, se buscarmos por algum de nossos aparelhos ópticos,
podemos nos deparar com a belíssima visão de
Uma nebulosa planetária com uma estrela central muito brilhante
http://hubblesite.org/gallery/wallpaper/pr1998039a/1440x960_wallpaper/
VELA, EM ARGO NAVIS, O NAVIO
Mario Jaci Monteiro - As Constelações, Cartas Celestes
Mario Jaci Monteiro - As Constelações, Cartas Celestes
Mario Jaci Monteiro - As Constelações, Cartas Celestes
VELA
Posicionamento:
Ascensão Reta 8h2m / 11h24m Declinação -37o.0 / -57o.0
Mito:
Esta constelação representa o navio no qual Jasão trouxe o Velocino de Ouro para Colquita - e dizem que foi o primeiro navio a ser construído.
História:
Esta constelação, o Navio, fazia parte do grupo de 48 constelações relacionado por Ptolomeu. Porém, La Caille dividiu o Navio em
Carina, Vela e Puppis: Quilha, Vela e Popa
Algumas Informações Interessantes acerca esta Constelação:
Aglomerados abertos 2670 e 2391 e 2547
As estrelas Kapa e Delta Velorum formam a Falsa Cruz juntamente com as estrelas Iota e Epsilon Carinae .
Fronteiras:
Algumas Estrelas
e alguns objetos interessantes, em Vela:
e alguns objetos interessantes, em Vela:
Al Suhail - Gamma Velorum - Sistema Múltiplo
Ascensão Reta 09h 07,3m - Declinação - 43o 21’
Magnitude visual 2,22 - Distância 750 anos-luz
Mastro, nome proveniente da expressão árabe Al Suhail al Muhlif, ou seja, o mastro do navio. Tal vocábulo também é empregado para designar as estrelas Zeta e Lambda Velorum.
Delta Velorum
Magnitude 1.95, com uma companheira de magnitude 5.1. Existe uma terceira companheira que é uma binária expectroscópica e com magnitude 10.
Markeb - Kappa Velorum
O Navio, do antigo asterismo árabe situado na constelação da Vela.
NGC I2391 - Aglomerado Aberto Vela
Ascensão Reta 08h39m Declinação -52o.59
Magnitude fotográfica global 2,6 Magnitude fotográfica da mais brilhante estrela 3,5
Distância kpc 0,15 Diâmetro 45’ Tipo Espectral B4
I2395 - Aglomerado Aberto Vela
Ascensão Reta 08h40m Declinação -48o.07
Magnitude fotográfica global 4,6 Magnitude fotográfica da mais brilhante estrela 10,1
Distância kpc 0,90 Diâmetro 20’ Tipo Espectral B2
NGC 3132 - Nebulosa planetária na fronteira entre a Vela e Antlia:
O ANEL DO SUL
O ANEL DO SUL
NGC 3132 é uma nebulosa planetária na direção da constelação de Vela. O objeto foi descoberto pelo astrônomo John Herschel em 1835, usando um telescópio refletor com abertura de 18,6 polegadas. Devido a sua moderada magnitude aparente (+9,2), é visível apenas com telescópiosamadores ou com equipamentos superiores.
http://pt.wikipedia.org/wiki/NGC_3132
 |
http://www.spacetelescope.org/static/archives/images/screen/opo9839a.jpg
NGC 3132 is a striking example of a planetary nebula.
This expanding cloud of gas, surrounding a dying star,
is known to amateur astronomers in the southern hemisphere as the 'Eight-Burst' or the 'Southern Ring' Nebula.
Credit:
Hubble Heritage Team (STScI/AURA/NASA/ESAhttp://www.spacetelescope.org/images/opo9839a/
|
| NGC 3132: Nebulosa do Anel Sul Créditos e direitos autorais : Hubble Legacy Archive, ESA, NASA; Processamento - Donald Waid | |
| |
http://apod.astronomos.com.br/apod.php?lk=ap130409.html
Esta é a nebulosa planetária NGC 3132.
Foi gerada após a morte de uma estrela semelhante ao Sol.
Mas a estrela que lhe deu origem não é a mais brilhante na imagem; a sua “mãe” é a anã branca menos brilhante que aparece na imagem próxima do centro da nebulosa.
NGC 3256, a distorted spiral galaxy in Vela
Image Credit: NASA, ESA, the Hubble Heritage Team (STScI/AURA)-ESA/Hubble Collaboration and A. Evans (University of Virginia, Charlottesville/NRAO/Stony Brook University)
NGC 3256 is a very bright, distorted spiral galaxy of more than 100,000 light-years across, located about 100 million light-years away from Earth in the southern constellation of Vela (Sails), while it is receding from us at approximately 2804 kilometers per second. It lies near, and is probably interacting with the barred spiral galaxies NGC 3256A, NGC 3256B en NGC 3256C, and belongs to the Hydra-Centaurus supercluster of galaxies.
Herbig Haro object HH 47, a stellar jet in Vela
Image Credit: J. Morse/STScI, and NASA/ESA
Herbig Haro object HH 47 is a bipolar stellar jet of 4.83 trillion kilometers long and 10 times the width of our Solar System located at the edge of the Gum Nebula, about 1140 light-years away in the southern constellation of Vela.
This unprecedented image of Herbig-Haro object HH 46-47 combines radio observations acquired with the Atacama Large Millimeter/submillimeter Array (ALMA) with much shorter wavelength visible light observations from ESO’s New Technology Telescope (NTT). The ALMA observations (orange and green, lower right) of the newborn star reveal a large energetic jet moving away from us, which in the visible is hidden by dust and gas. To the left (in pink and purple) the visible part of the jet is seen, streaming partly towards us.
Image Credit: ESO/ALMA (ESO/NAOJ/NRAO)/H. Arce. Acknowledgements: Bo Reipurth
Young stars are violent objects that eject material at speeds of as high as one million kilometers per hour. When this material crashes into the surrounding gas it glows, creating a Herbig-Haro object [1]. A spectacular example is named Herbig Haro 46-47 and is situated about 1,400 light-years from Earth in the southern constellation of Vela (The Sails). This object was the target of a study using ALMA during the Early Science phase, whilst the telescope was still under construction and well before the array was completed.
Exposed Cranium Nebula
http://www.spitzer.caltech.edu/uploaded_files/images/0009/7431/sig13-013_Sm.jpg
The brain-like orb called PMR 1 has been nicknamed the "Exposed Cranium" nebula by Spitzer scientists.
Position (undefined)
RA = 9h 28m 40.9s Dec = -49° 36' 26.6"
Field of View
5.5 x 5.5 arcminutes
Orientation
North is 62.4° right of vertical
Constellation
Vela http://www.spitzer.caltech.edu/images/5687-sig13-013-Exposed-Cranium-Nebula
The brain-like orb called PMR 1 has been nicknamed the "Exposed Cranium" nebula by Spitzer scientists.
- Credit
- NASA/JPL-Caltech/J. Hora (Harvard-Smithsonian CfA)
About the Object
- Name
- PMR1 • PN G272.8+01.0 • Exposed Cranium Nebula
- Type
- Nebula > Type > Planetary
- Distance
- 5,000 Light Years
Julius Schiller, Coelum stellatum Christianum, 1627
Os desenhos formados pelas estrelas
– As Constelações -
são como janelas que se abrem para a infinitude do universo
e que possibilitam nossa mente a ir percebendo
que existe mais, bem mais, entre o céu e a terra...;
bem como percebendo que o caos,
vagarosamente,
vai se tornando Cosmos
e sendo por nossa mente conscientizado.
Quer dizer, nossa mente é tão infinita
quanto infinito é o Cosmos.
– As Constelações -
são como janelas que se abrem para a infinitude do universo
e que possibilitam nossa mente a ir percebendo
que existe mais, bem mais, entre o céu e a terra...;
bem como percebendo que o caos,
vagarosamente,
vai se tornando Cosmos
e sendo por nossa mente conscientizado.
Quer dizer, nossa mente é tão infinita
quanto infinito é o Cosmos.
COM UM ABRAÇO ESTRELADO,
Janine Milward
Hemisphaerium Coeli Australe in quo Fixarum loca secundum Eclipticae ductum ad anum 1730 . .
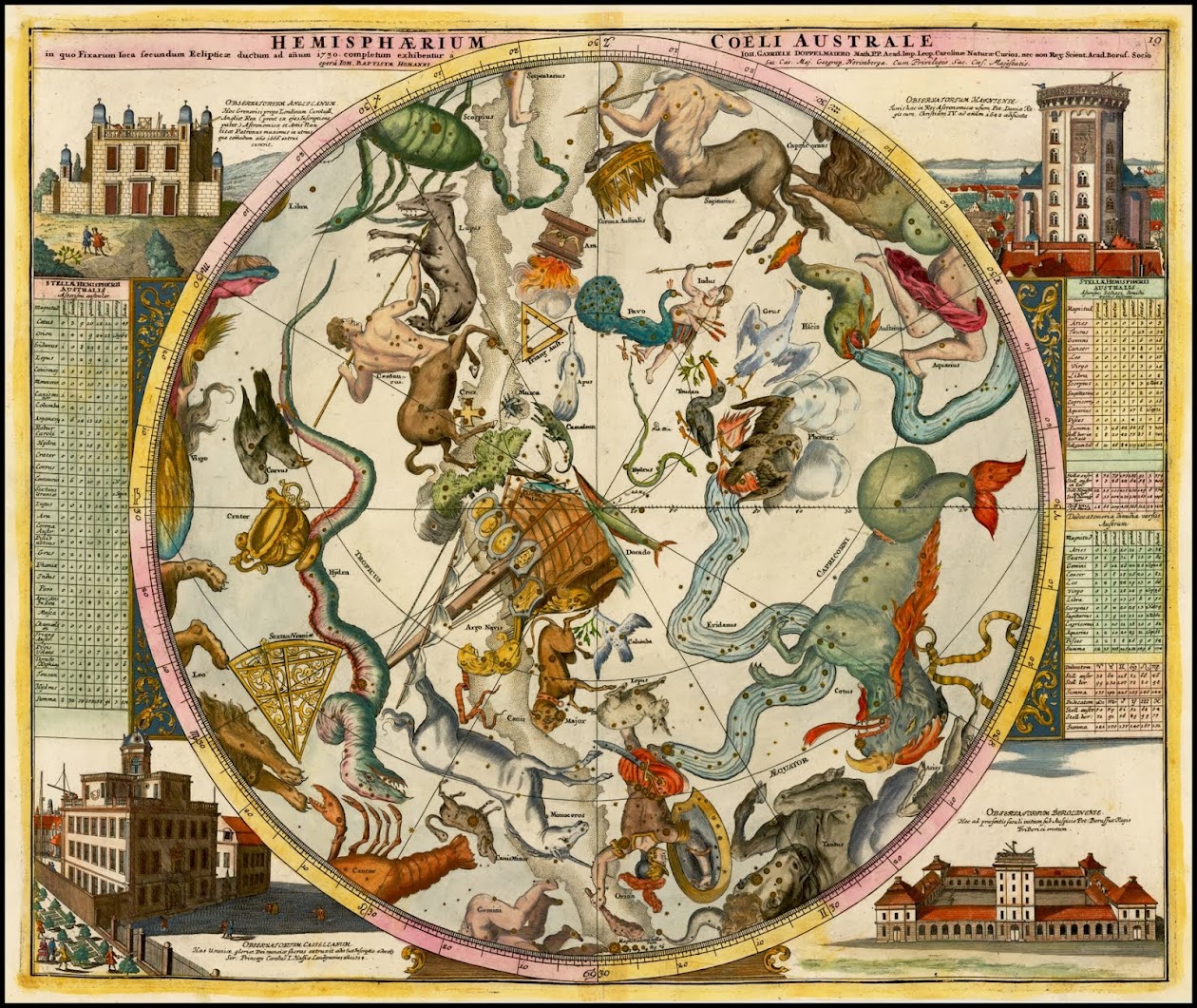
Nice example of Johanne Doppelmayr's map of the Southern Skies, with the constellations shown and the various stars illustrated in gold. Dopplemayr's decorative celestial chart illustrates the southern sky form the south ecliptic pole to ecliptic. The constellations are delineated based upon the catalogue of Johannes Hevelius and include Orion, Scorpio, Taurus, Eridanus and the Southern Cross. The constellations include some unusal additions, including the Peacock, Toucan, and a lovely unicorn called Monoceros.
http://hubblesite.org/gallery/wallpaper/pr1998039a/1440x960_wallpaper/









